How Algorithms Works: Have you ever considered what powers your favorite apps, websites, and devices? It’s the algorithms.
Algorithms are running the show. TikTok has great recommendations. Google answers questions in seconds. But how do they work? What’s their deal? It might help you to know if I can explain it step by step.
What Are Algorithms, and Why Should You Care?
An algorithm is a set of rules.
Think of it like this: If A happens, do B.
Simple, right?
But, here’s the kicker: algorithms are so fast and scalable that they make humans look like snails.
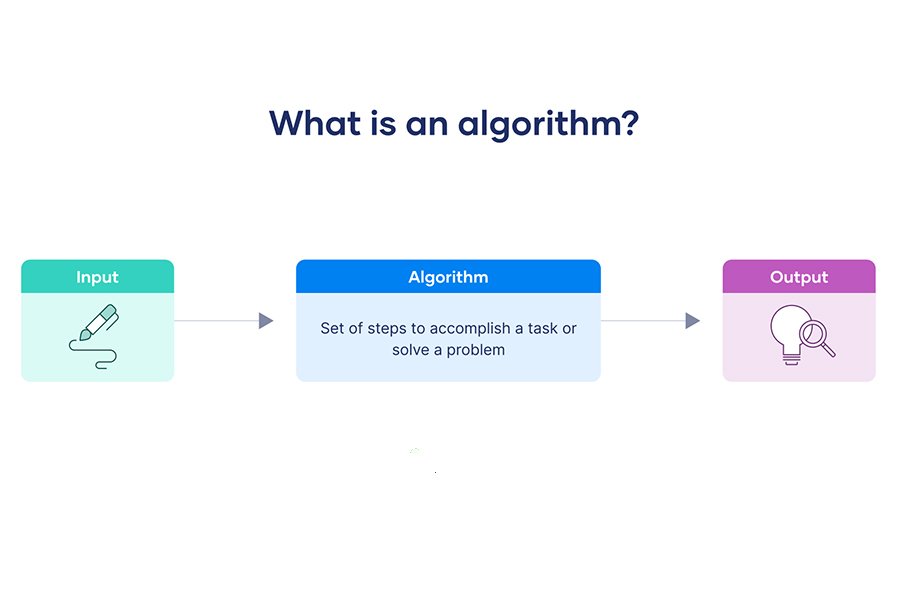
Let’s bring it down to earth with an example. Imagine you want to bake cookies.
- You gather ingredients (input).
- You follow the recipe (process).
- You end up with cookies (output).
That’s an algorithm in action—input, process, output.
Why should you care? Because algorithms shape almost everything in your digital life:
- Your social media feed: Decide which posts you see and in what order.
- Online shopping: Suggests products based on what you have browsed.
- Streaming services: I recommend shows that keep you glued to the screen.
Without algorithms, your experience online would be a hot mess.
How Do Algorithms Actually Work?
At their core, algorithms follow these three steps:
- Take input: They gather data—like your search query or browsing history.
- Process data: They analyze it based on pre-defined rules.
- Spit-out output: You get recommendations, answers, or results.
Let’s make this less abstract.
Example: How Netflix’s algorithm decides what you watch next
- Input: What shows you’ve watched, your likes, and your watch history.
- Processing: Netflix compares your data to millions of other users.
- Output: It recommends a binge-worthy series. It’s based on what similar users liked.
Cool, huh?
The Different Types of Algorithms: What They Do
Some algorithms are better than others. Here are the main ones you interact with daily:
- Search Algorithms
When you type something into Google, it uses a search algorithm to find and rank the best answers.
How it works:
- Crawling: Scans the Internet for new and updated pages.
- Indexing: Stores these pages in a giant library.
- Ranking: Decides which pages are the most relevant to your query.
- Sorting Algorithms
These arrange things in order, like sorting emails by date or filtering items by price on Amazon.
- Recommendation Algorithms
Spotify, YouTube, and Instagram use these to suggest content you’ll like. They analyze your behavior and match it with patterns from other users.
- Machine Learning Algorithms
These take things to the next level. They learn from data and improve over time. They rely on patterns, not explicit programming. Example: self-driving cars. They use algorithms to understand traffic, pedestrians, and road signs. They get better the more they drive.
Why Are Algorithms So Important?
Without algorithms, the digital world wouldn’t slow down—it would stop. Here’s why they’re crucial:
- Speed: Algorithms process insane amounts of data faster than any human ever could.
- Consistency: They follow rules with flawless adherence on each occasion. No mood swings or “off days.”
- Scalability: Algorithms don’t care if they’re handling 10 tasks or 10 billion.
Real-Life Impact Examples
- Healthcare: Algorithms analyze medical data to detect diseases earlier than doctors.
- Finance: Algorithms handle stock trading, processing millions of transactions in seconds.
- Marketing: They help brands target the right audience with precision.
The Downside of Algorithms
But hold up—they’re not perfect. Here’s where algorithms can go sideways:
- Bias
The quality of algorithms depends on the data used to train them. If biased data exists, the algorithm will also show bias.
Example: Facial recognition systems that struggle with accuracy for certain skin tones.
- Lack of Transparency
Not possible to remove the adverb. Algorithms are often “black boxes.” You don’t know how they work, and companies don’t always explain them.
- Data Privacy
Algorithms collect a ton of data to do their job. But that raises questions: Who is using your data, and for what purpose?
Can You Outsmart Algorithms?
Here’s the thing: you can’t completely “beat” an algorithm, but you can work with it.
For Social Media
Want your content to reach more people?
- Publish on a consistent schedule.
- Engage with your audience (likes, comments, shares).
- Use trending hashtags.
For SEO
Trying to rank your website on Google?
- Incorporate relevant keys in a way that feels instinctive.
- Create high-quality, original content.
- Optimize for mobile devices and fast loading speeds.
For E-commerce
Selling products online?
- Use clear product descriptions.
- Add lots of reviews.
- Offer discounts to encourage purchases.
Play by the rules, and you’ll see results.
How Web Solve Tech Leverages Algorithms
At Web Solve Tech, we don’t use algorithms—we master them.
Our Process:
- Data Analysis: We dig deep into customer behavior to uncover trends and insights.
- Automation: Why waste time on repetitive tasks? We build systems to handle them for you.
- We use algorithms to optimize your SEO, social media, and email campaigns. This gives you better results faster.
What that means for you:
- Higher traffic to your site.
- More engagement on your posts.
- Increased sales and conversions.
Ready to see the power of algorithms in action? We’ve got you covered.
Conclusion
Algorithms might sound like they’re running the world—and to some extent, they are. But they’re not magic, and they’re not unbeatable.
When you know how these shortcuts are formed then you can work to your benefits. Knowing the rules gives you an edge. It helps with your business, your content, and your Netflix recommendations.
We specialize in helping businesses unlock the power of algorithms. Want to know how we can help you? Let’s talk.